What Is Forex?
The foreign exchange market is the “place” where currencies are traded. Currencies are important to most people around the world, whether they realize it or not, because currencies need to be exchanged in order to conduct foreign trade and business. If you are living in the U.S. and want to buy cheese from France, either you or the company that you buy the cheese from has to pay the French for the cheese in euros (EUR). This means that the U.S. importer would have to exchange the equivalent value of U.S. dollars (USD) into euros. The same goes for traveling. A French tourist in Egypt can’t pay in euros to see the pyramids because it’s not the locally accepted currency. As such, the tourist has to exchange the euros for the local currency, in this case the Egyptian pound, at the current exchange rate.
The need to exchange currencies is the primary reason why the forex market is the largest, most liquid financial market in the world. It dwarfs other markets in size, even the stock market, with an average traded value of around U.S. $2,000 billion per day. (The total volume changes all the time, but as of August 2012, the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) reported that the forex market traded in excess of U.S. $4.9 trillion per day.)
There is no central marketplace for foreign exchange.
Rather, currency trading is conducted electronically over-the-counter (OTC), which means that all transactions occur via computer networks between traders around the world, rather than on one centralized exchange. The market is open 24 hours a day, five and a half days a week, and currencies are traded worldwide in the major financial centers of London, New York, Tokyo, Zurich, Frankfurt, Hong Kong, Singapore, Paris and Sydney – across almost every time zone. This means that when the trading day in the U.S. ends, the forex market begins anew in Tokyo and Hong Kong. As such, the forex market can be extremely active any time of the day, with price quotes changing constantly.
Spot Market and the Forwards and Futures Markets
There are actually three ways that institutions, corporations and individuals trade forex: the spot market, the forwards market and the futures market. The forex trading in the spot market always has been the largest market because it is the “underlying” real asset that the forwards and futures markets are based on. In the past, the futures market was the most popular venue for traders because it was available to individual investors for a longer period of time. However, with the advent of electronic trading, the spot market has witnessed a huge surge in activity and now surpasses the futures market as the preferred trading market for individual investors and speculators. When people refer to the forex market, they usually are referring to the spot market. The forwards and futures markets tend to be more popular with companies that need to hedge their foreign exchange risks out to a specific date in the future.
What is the spot market?
More specifically, the spot market is where currencies are bought and sold according to the current price. That price, determined by supply and demand, is a reflection of many things, including current interest rates, economic performance, sentiment towards ongoing political situations (both locally and internationally), as well as the perception of the future performance of one currency against another. When a deal is finalized, this is known as a “spot deal”. It is a bilateral transaction by which one party delivers an agreed-upon currency amount to the counter party and receives a specified amount of another currency at the agreed-upon exchange rate value. After a position is closed, the settlement is in cash. Although the spot market is commonly known as one that deals with transactions in the present (rather than the future), these trades actually take two days for settlement.
What are the forwards and futures markets?
Unlike the spot market, the forwards and futures markets do not trade actual currencies. Instead they deal in contracts that represent claims to a certain currency type, a specific price per unit and a future date for settlement.
Why is the Forex market so popular?
Being a Forex trader offers the most amazing potential lifestyle of any profession in the world. It’s not easy to get there, but if you are determined and disciplined, you can make it happen. Here’s a quick list of skills you will need to reach your goals in the Forex market:
Ability – to take a loss without becoming emotional
Confidence – to believe in yourself and your trading strategy, and to have no fear
Dedication – to becoming the best Forex trader you can be
Discipline – to remain calm and unemotional in a realm of constant temptation (the market)
Flexibility – to trade changing market conditions successfully
Focus – to stay concentrated on your trading plan and to not stray off course
Logic – to look at the market from an objective and straight forward perspective
Organization – to forge and reinforce positive trading habits
Patience – to wait for only the highest-probability trading strategies according to your plan
Realism – to not think you are going to get rich quick and understand the reality of the market and trading
Savvy – to take advantage of your trading edge when it arises and be aware of what is happening in the market at all times
Self-control – to not over-trade and over-leverage your trading account
As traders, we can take advantage of the high leverage and volatility of the Forex market by learning and mastering and effective Forex trading strategy, building an effective trading plan around that strategy, and following it with ice-cold discipline.
Who trades Forex and why?
Banks – The interbank market allows for both the majority of commercial Forex transactions and large amounts of speculative trading each day. Some large banks will trade billions of dollars, daily. Sometimes this trading is done on behalf of customers, however much is done by proprietary traders who are trading for the bank’s own account.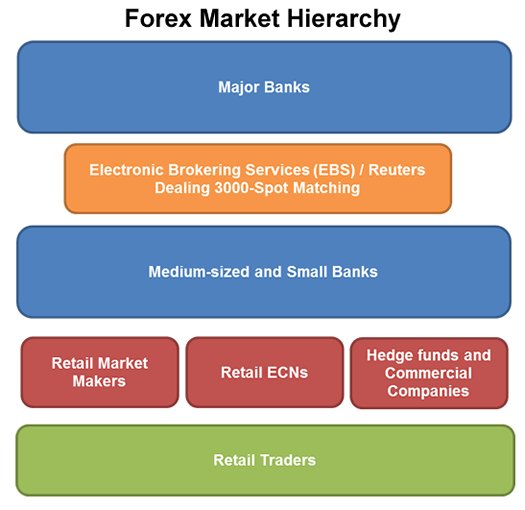
Companies – Companies need to use the foreign exchange market to pay for goods and services from foreign countries and also to sell goods or services in foreign countries. An important part of the daily Forex market activity comes from companies looking to exchange currency in order to transact in other countries.
Governments / Central banks – A country’s central bank can play an important role in the foreign exchange markets. They can cause an increase or decrease in the value of their nation’s currency by trying to control money supply, inflation, and (or) interest rates. They can use their substantial foreign exchange reserves to try and stabilize the market.
Hedge funds – Somewhere around 70 to 90% of all foreign exchange transactions are speculative in nature. This means, the person or institutions that bought or sold the currency has no plan of actually taking delivery of the currency; instead, the transaction was executed with sole intention of speculating on the price movement of that particular currency. Retail speculators (you and I) are small cheese compared to the big hedge funds that control and speculate with billions of dollars of equity each day in the currency markets.
Individuals – If you have ever traveled to a different country and exchanged your money into a different currency at the airport or bank, you have already participated in the foreign currency exchange market.
Investors – Investment firms who manage large portfolios for their clients use the Fx market to facilitate transactions in foreign securities. For example, an investment manager controlling an international equity portfolio needs to use the Forex market to purchase and sell several currency pairs in order to pay for foreign securities they want to purchase.
Retail Forex traders – Finally, we come to retail Forex traders (you and I). The retail Forex trading industry is growing everyday with the advent of Forex trading platforms and their ease of accessibility on the internet. Retail Forex traders access the market indirectly either through a broker or a bank. There are two main types of retail Forex brokers that provide us with the ability to speculate on the currency market: brokers and dealers. Brokers work as an agent for the trader by trying to find the best price in the market and executing on behalf of the customer. For this, they charge a commission on top of the price obtained in the market. Dealers are also called market makers because they ‘make the market’ for the trader and act as the counter-party to their transactions, they quote a price they are willing to deal at and are compensated through the spread, which is the difference between the buy and sell price (more on this later).
Click to Check spreads offered by various brokers in the world.
